Search
Traffic Control
- Traffic Signal Upgrade: Work which involves any one of the following for non-emergency purposes; the installation of a new controller and cabinet, rewiring the entire signal, installing all new poles or changing the layout of the signal.
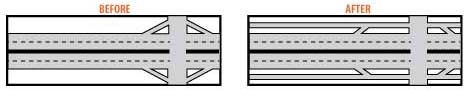
- Restricted Crossing U-Turn (RCUT) Intersection: a non-traditional intersection system that utilizes a combination of one partial median opening and two directional median openings. This type of intersection is typically the crossing of major and minor arterials where the left turn moves are relatively high. The openings must be appropriately spaced with one directional U-turn opening or one partial median opening on each side of the partial median opening. The distance between two of these systems is also critical. The intersection and U-turns may be unsignalized or signalized, depending on volumes.
- Median U-Turn (MUT) Intersection: the use of two or four directional U-turn openings, placed on each side of an intersection, combined with the prohibition of all left turns at the intersection. This type of intersection is typically the crossing of two major arterials where the through move is heavier than the left turns. All through movements and right turns at the intersection are permitted. The openings must be appropriately spaced with one directional median opening on each side of the partial median opening. The distance between two of these treatments is also critical. The main intersection is typically signalized and the U-turns may be unsignalized or signalized, depending on volumes.
- Full Access Traffic Signal: a traffic signal where all approaches are allowed to turn left out and left in.
Traffic Control Design
Access Management
As roadways develop and traffic increases, congestion occurs, adding to delays and the probability of crashes. To alleviate these problems, the use of access management is practiced.
What is access management?
Access management is a technique used to improve efficiency and safety on roadways. It aims at focusing on the location, spacing, design of entrances, street intersections, median openings, and traffic signals by minimizing conflict points.
What are the benefits of access management?
- Reduces congestion
- Enhances safety by eliminating conflict points
- Spurs economic development by promoting efficient movement of goods and services
What are conflict points?
Conflict points are areas where traffic flow is disrupted or points where motorists crossing, merging or diverging from a road or driveway may collide with another motorist. See diagram below.
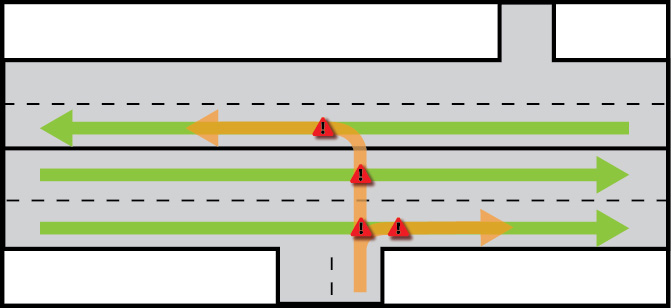
What are frequently used access management treatments?
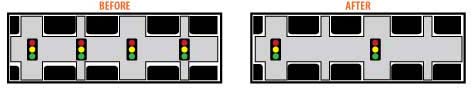
Traffic signal spacing: Proper access management requires appropriate traffic signals and intersection spacing. Signals should be at a minimum of one-half mile apart. Intersection spacing along thoroughfares and streets should range from half a mile to two miles.
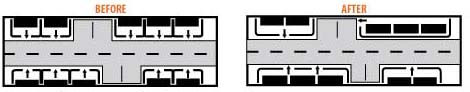
Driveway consolidating: Maintaining adequate spacing between commercial driveways is a critical aspect of access management. Research shows that roadways with a large number of closely spaced driveways are more problematic than those where driveway access is more limited.
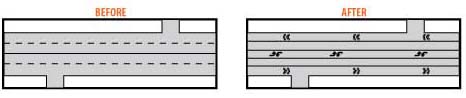
Turning lanes: Exclusive turning lanes eliminate vehicles from obstructing free flowing traffic. This includes dedicated left- and right-turn lanes, as well as U-turns, and roundabouts.
Median redesign: One of the most effective access management tools is to use median treatments like raised medians.
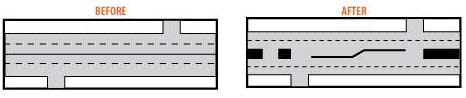
Frontage roads: These are roadways that are constructed generally parallel to a freeway or other highway. They have the ability to serve local traffic and keep it from congesting the freeway mainlanes, in addition to moving traffic during crash situations on the mainlanes.
How does access management affect businesses?
Studies show that businesses such as doctor’s offices and specialty retail stores are unaffected by access management. Although pass-by businesses (restaurants, gas stations) may be affected, studies have shown that as long as reasonable access is provided, there are no negative impacts to business. In fact, a road that flows better leads to more vehicles passing by and seeing your business. According to FHWA, "Access is not the primary reason that businesses survive or fail. In fact, access is one of the lesser factors that customers will consider when weighed against price, service, product, and store amenities."
Access Connections
Access Connections to Controlled Access Highways
EDSM I.4.3.2 Request for New or Modified Access on Control of Access Facilities
FHWA Requirements Access Policy Update 9-2009
Interstate Access Policy Update 5-2017
Interstate Access Policy Update Memo 5-2017
Access Connections to Non-State Local Roads
Contact your local government
Access Connections to Other State Highways
Access Connection Permits Rule - Ch 15 in LA Administrative Code Title 70, Transportation
Access Connections: Rule & Policy
EDSM IV.2.1.4 Median Openings on Divided Multi-Lane Roadways
Access Connections Policy 12-2013
Access Management Topics From Statewide Meetings
Access Management Brochure Business
Access Management Brochure Public
Access Connections Traffic Impact
Traffic Impact Rule Comments From Statewide Meetings
Roundabouts
Roundabouts are one-way, circular intersections designed to improve safety and efficiency for motorists, bicyclists and pedestrians. In a roundabout, traffic flows counterclockwise around a center island. A roundabout redirects some of the conflicting traffic, such as left turns, which cause crashes at traditional intersections. This is because drivers enter and exit the roundabout through a series of right-hand turns.
A well-designed roundabout can improve safety, operations and aesthetics of an intersection. Greater safety is achieved primarily by slower speeds and the elimination of more severe crashes and operation is improved by smooth-flowing traffic with less stop-and-go than a signalized intersection. Aesthetics are enhanced by the opportunity for more landscaping and less pavement.
Over the past few years, DOTD has constructed roundabouts across Louisiana in an effort to increase safety and traffic flow at select locations.
Roundabouts Design in Road Design Manual Chapter 6
Roundabout Info And Instructions
Roundabout List
Roundabout Map
Work Zones
Policies and Guidelines
Policy For Police In Work Zones
Interstate Lane Closures Queue Analysis
Research Papers
Recommended Procedures For The Safety Performance Evaluation Of Highway Feature
A Procedure For Assessing And Planning Nighttime Highway Construction And Maintenance
Guidelines For Design And Operation Of Nighttime Traffic Control For Highway Maintenance And Construction
Traffic Control Devices
Pavement Markings
Signing
DOTD Sign Manual
- Section 2D.2 5/1/2007 Gateway Sign on Interstate and Non-Interstate Highways
- Section 2D.3 3/2/2006 Use of Pharmacy Signs on Interstate Highways
- Section 2E.2 5/1/2007 Tourist Information and Welcome Center Signing
Interstate Highway Control Cities
Visit our Maps page for information about Authorized Interstate Crossovers.
